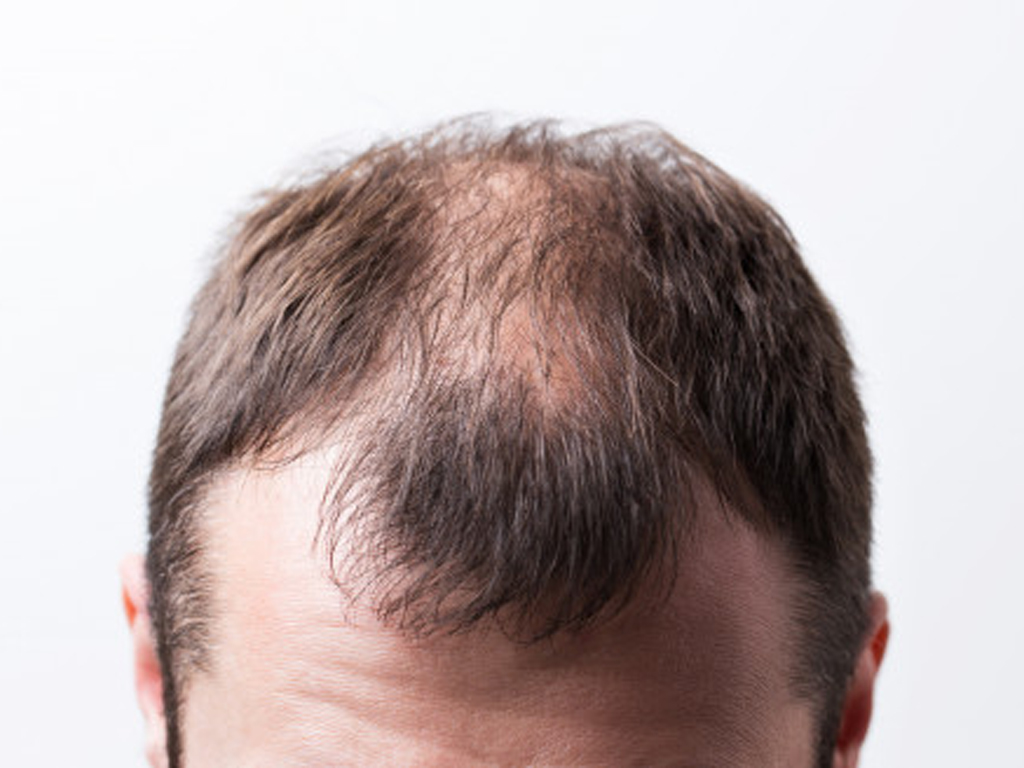
How well do you know types of alopecia? This disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair to fall out in lumps the size of a quarter.
Table of Contents |
The amount of hair loss varies from person to person. Some people only lose a few spots, some lose a lot, and sometimes the hair grows back but then falls out again. In others, the hair grows back forever.
Some types of this disease are related to genetic, lifestyle or environmental factors, as well as mental conditions that lead to hair loss. It is not contagious, although it can sometimes be a sign of other health problems. Treatment for most types is the same and may include oral medications and topical treatments.
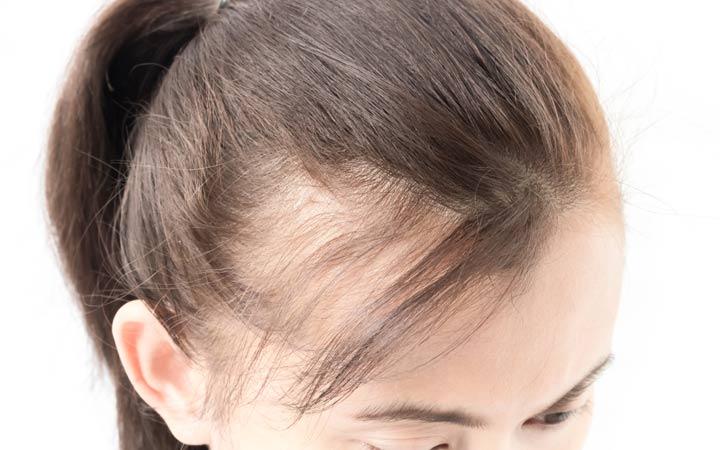

Types of alopecia
Anything that disturbs the natural and healthy hair growth cycle can lead to this disease. Some types are avoidable, but others can affect anyone at any age. Your family history, age, gender and race can be factors in getting this type of disease.
Alopecia areata
The main symptom of alopecia areata is hair that falls out in patches, usually on the scalp. In fact, one or more round bald spots are observed on the scalp. But this type is not limited to the scalp and can involve eyebrows, eyelashes and other parts of the body.
In this disease, the body mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles that cause hair growth. This damage causes hair loss in different parts of the body.
Persistent patchy alopecia areata
When patchy hair loss continues but does not improve or worsens over time, the cause is alopecia areata.
What is alopecia totalis?
When the entire scalp becomes bald and the hair falls out, like other forms of it, this condition is linked to an abnormal immune system response. However, researchers are still trying to figure out the exact cause.
Alopecia areata
As its name suggests, it causes complete hair loss. This disease includes the scalp and the rest of the body. As with other autoimmune diseases, the reason why some people get it and others don’t is still unknown.
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata of the coin type is also known as telogen effluvium. This type is different from the others because the hair becomes thinner and instead of falling out in patches, it falls out in scattered areas all over the skin. In rare cases, similar patterns of hair loss occur in other areas of the body due to extreme stress, sudden hormonal changes, and side effects of chemical medications.
Alopecia areata
This disease model is a type of alopecia areata that mostly affects the sides and back of the head. This autoimmune disorder occurs mostly at young ages and affects young age groups.
Androgenic alopecia
This type of disease is common and affects people of all genders, and women may also be affected by this disease.
male pattern
Male pattern baldness usually begins with receding hairline above the forehead or hair loss at the crown of the head. The sides and bottom of the head are usually the last areas to lose hair when affected.
female pattern
Female pattern baldness differs from male pattern baldness in that it usually begins with thinning of the hair along the midline or obliques. The dividing line in this pattern may have more shedding, but complete baldness is rare.
Cicatricial alopecia
Experts do not fully understand the causes of this type, although this inflammatory condition can sometimes develop after the skin is damaged by a burn or severe infection. Hair loss may occur slowly in patches or more rapidly in larger areas. The skin underneath may also be itchy or inflamed.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia
This disorder is a form of lichen planopilaris disease. It usually causes a slow but progressive loss of hair just above the forehead. Eyebrows and eyelashes may also be affected.
Traction alopecia
This type of disease is caused by repeated pulling or tightening of hair in one direction.
Alopecia areata
This type is an autoimmune disease that causes it to fall out in small circular patches. In some cases, as the disease progresses, the patches overlap. However, it is difficult to predict the rate of hair loss.
Postpartum alopecia
A rapid and significant decrease in estrogen levels after childbirth can lead to a disease called postpartum alopecia. This disease is not a normal hair loss. The reason is actually hair loss following increased hair growth that can occur during pregnancy. Within a few months, regular hair growth usually resumes.
Common types of alopecia in men
Men suffer from hair loss more than women. In addition to genetic triggers and the immune system for hair loss, hormonal factors, especially the decrease in the level of the male sex hormone hydrotestosterone, are involved in male hair loss.
The most common types that may affect men are: alopecia areata, androgenic and barba.
Alopecia in women
Hair loss in women is significantly less than in men. But the most common types that women may experience are: alopecia areata, postpartum, androgenic and stretch alopecia.
Alopecia in children
Children experience much less hair loss than adults. Although certain types of this disease can affect children. Among them are: alopecia areata, which often begins in adolescence, and alopecia ophiiasis.
Alopecia treatment
While there is no definitive cure for this condition, several treatment options may help regrow hair or at least slow or stop hair loss. In addition to treatment with chemical drugs, among the common treatments that are used for it are:
Microneedling
Microneedling is a relatively new treatment for stimulating new hair growth. This treatment involves puncturing the scalp with tiny needles to stimulate the production of collagen (a type of protein) that can restore hair growth. Types of alopecia that can be treated with microneedling are:
- Alopecia areata
- Androgenic alopecia
- Alopecia areata
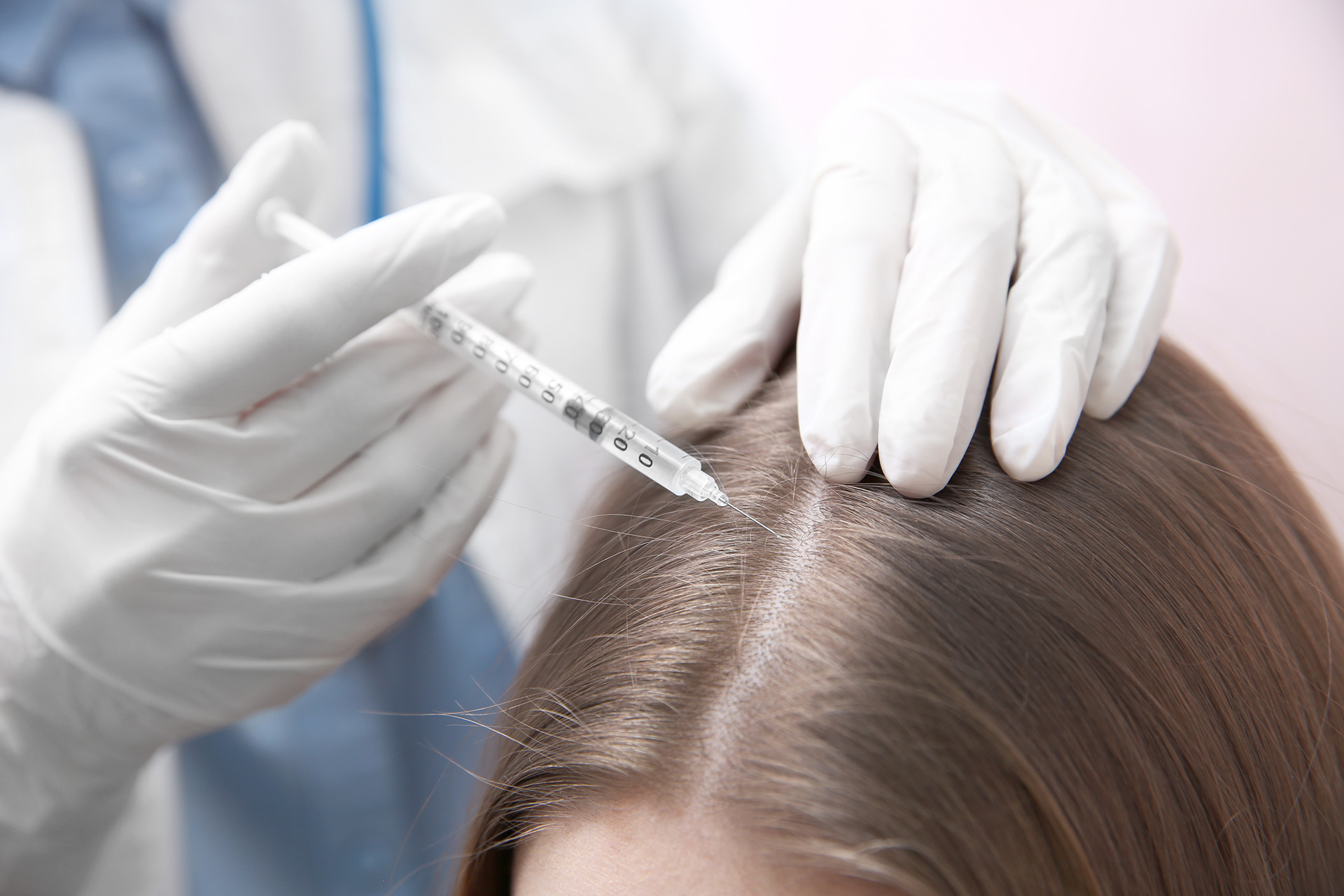
PRP
Plasma is the part of your blood that contains special proteins that help blood clot. It also contains proteins that help in cell growth. PRP is made by separating plasma from blood and concentrating it. Injecting PRP into the damaged tissues of the body stimulates the growth of new healthy cells and promotes healing.
Injecting PRP into the scalp makes the scalp healthier and thus creates a better environment for hair growth.
hair transplant
Hair transplantation is a local treatment for alopecia. In general type of alopecia, this treatment is not generally applicable and may not cover the entire bald area, but hair transplantation can be tried for alopecia areata.
Conclusion
Most types of this disease occur without warning and progress at an unpredictable rate. In some cases, hair growth returns on its own. But in most cases, treatment is necessary to restore the hair. If you notice hair loss anywhere on your body, see a dermatologist to discuss treatment options.
Suggestion of Serenity Beauty Clinic Dubai for further study
-
Wrinkle Injection
-
Filler
-
Hydrafacial
-
Slimming
-
Hollywood Smile dubai
-
Laser Skin
-
Aquagold
-
Body Piercing
-
Veneers dubai
-
Invisalign
-
Composite Filling
-
Anti Cellulite Massage
-
Teeth Whitening dubai
-
Laser Tattoo Removal
-
PRP dubai
-
Laser Hair Removal
-
Mesotherapy
-
Mesotherapy For Face
-
Mesotherapy For Hair
-
Lip Filler
-
Thread Lift
-
Nose Filler
-
Hair Filler
-
Hair PRP
-
Profhilo Injection